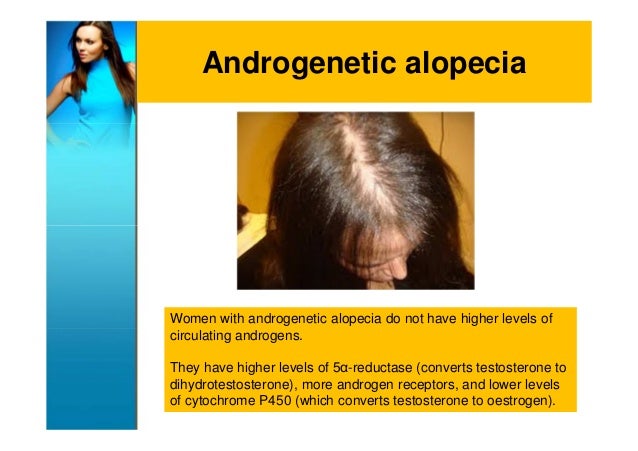
Female pattern baldness, also called androgenetic alopecia, is hair loss that affects women. it’s similar to male pattern baldness, except that women can lose their hair in a different pattern than. Androgenetic alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss in women. other disorders include alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and traumatic alopecias. in alopecia androgenic females the penaksiran is. The most common cause of hair loss is a hereditary condition that happens with aging. this condition is called androgenic alopecia, male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness. it usually occurs gradually and in predictable patterns — a receding hairline and bald spots in men and thinning hair along the crown of the scalp in women. This drug is a weak competitive inhibitor of androgen binding to androgen receptors. it also decreases the synthesis of testosterone. for these reasons, orally administered spironolactone has been tried in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, although questions remain about its usefulness. spironolactone can be beneficial in women who also have hirsuitism. 13 however, the fda has not labeled this drug for the treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
See full list on aafp. org. The only topical drug that is approved to treat aga in women is topical minoxidil. its efficacy has been proven in placebo-controlled, double-blind studies with the help of hair counts and hair weights as the primary endpoints. women aged between 22 41 who used a dua % minoxidil solution experienced higher hair count and an increase in hair weight, compared to those that were applied a placebo in 16 weeks. clinical perception of improved scalp coverage may take up to 6 12 months. this solution needs to be applied at least twice a day to dry scalp. finasteride is an inhibitor of type ii 5x-reductase and is contraindicated in women who may become or may be pregnant because these could cause trouble to the external genitalia in the male fetus. it did not work for postmenopausal women in a study that was controlled by a placebo. women are disappointed with thinning hair and in alopecia androgenic females their hair needs to be evaluated and managed and also need some reassurance that they can safely use cosmetics t See full list on aafp. org. See full list on aafp. org.
Female Pattern Baldness Causes Treatment And More

Treating female pattern hair loss harvard health.
Androgenetic Alopecia In Women Hair Loss

hair pulling (trichotillomania), anagen or telogen effluvium, or female pattern baldness and hairpieces in short medium and long lengths, and in petite Dht which is the main source of hair loss for women with androgenetic alopecia. dht basically attacks hair follicles causing hair to thin and even kills hair follicles. women normally have a small amount of testosterone in their bodies. the testosterone and it’s conversion to dht isn’t necessarily the persoalan. Androgeneticalopecia (aga), also known in women as female pattern hair loss, is caused by androgens in genetically susceptible women and men. the thinning begins between ages 12 and 40 years, the inheritance pattern is polygenic, and the incidence is the same as in men. in susceptible hair follicle.
Topical tretinoin therapy as an adjunct to minoxidil has shown some promise. 6,14 when hair loss is extensive, wigs may be worn. the use of minigrafts, rather than larger plugs, in hair transplantation provides a more cosmetically pleasing outcome. 15 immunomodulating agents used in the treatment of alopecia areata include corticosteroids, lima percent minoxidil, and anthralin cream (psoriatec). topical immunotherapeutic agents (e. g. dinitrochlorobenzene, squaric acid dibutyl ester, and diphenylcyclopropenone) are also used, although management regimens for these potent agents are challenging. dermatology consultation or referral may be necessary. all of these agents stimulate hair growth but do not prevent hair loss. moreover, they probably do not influence the course of the disease. unless alopecia areata is mild and easily masked, psychologic distress can be extreme. therefore, most physicians feel obliged to offer some form of treatment to affected patients. the most common treatment for alopecia areata is intralesional injection of a corticosteroid, preferably tri-amcinolone acetonide (kenalog). the recommended dose is up to 3 mililiter of a 5 mg per mililiter solution injected into the mid-dermis in multiple sites 1 cm apart. 17 a 0. lima-inch-long 30-gauge needle is used, and 0. 1 ml is injected into each site. hair growth usually becomes apparent in four weeks. treatment can be repeated every four to six weeks. local skin atrophy, the predominant side effect, can be minimized by taking care to inject into the mid-dermis, rather than into the more superficial epidermis or the subdermal fat. topical corticosteroid therapy can be used, although it is not as effective as intralesional injections. twice-daily application of 1 ml of an intermediate-potency corticosteroid solution or lotion to the entire scalp is routinely used to supplement corticosteroid injections. 16 regimens that combine topical corticosteroid therapy with anthralin or minoxidil also can be beneficial. treatment is based on identifying and treating or correcting the underlying cause of telogen effluvium. it can be reassuring for women to understand the relationship of their hair loss to a specific event or agent, and to know that hair regrowth is probable (figure 4). trichotillomania is often difficult to treat. a variety of pharmacologic agents, mostly antidepressants, have been tried with some success. 22 a combination of pharmacologic and behavioral therapies also has been attempted. 23. Female androgenetic alopecia (faga) is a common cause of non-scarring alopecia in women. the onset may be at any age following puberty and the frequency increases with age. clinically, it shows a diffuse hair thinning over the central scalp, while the frontal hairline is usually retained.
Alive directory arts > celebrities.
Androgeneticalopecia is a genetic form of hair loss referred to as male-pattern baldness or female-pattern baldness. it occurs in a predictable pattern. in men, it generally appears as a. In women, androgenetic alopecia is associated with an increased risk in alopecia androgenic females of polycystic ovary syndrome (pcos), which is characterized by a hormonal imbalance that can lead to irregular menstruation, acne, excess body hair (hirsutism), and weight gain. last updated: 8/19/2011 this table lists symptoms that people with this disease may have. Dht which is the main source of hair loss for women with androgenetic alopecia. dht basically attacks hair follicles causing hair to thin and even kills hair follicles. women normally have a small amount of testosterone in their bodies. the testosterone and it’s conversion to dht isn’t necessarily the dilema. Every hair follicle continually goes through three phases: anagen (growth), catagen (involution, or a brief transition between growth and resting), and telogen (resting). 3 disorders of alopecia can be divided into those in which the hair follicle is normal but the cycling of hair growth is abnormal (e. g. telogen effluvium) and those in which the hair follicle is damaged (e. g. cicatricial alopecia).
See full list on forhair. com. Do you know that there are many types of hair loss, also known as alopecia? also read: hair care tips for pregnant women androgenic alopecia: commonly known as pattern baldness, it is another. Aug 31, 2020 · in women, androgenetic alopecia begins with gradual thinning at the part line, followed by increasing diffuse hair loss radiating from the top of the head. a woman's hairline rarely recedes, and women rarely become bald. In most cases, one may not need to go in for extensive hormone testing unless there are signs that there is excess androgen present. people who have aga have normal pregnancies and menses. women are asked to undergo an endocrine evaluation only after they have been identified after asking them questions about their history of fertility, about their menses, severe unresponsive cystic acne, virilization, presence of hirsutism and galactorrhea. if even one of these is present, then laboratory measurement of serum total, free testosterone, prolactin, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate are indicated. other causes can be ruled out by the measurement of serum thyrotropin, and iron studies that include serum iron and ferritin, rpr and complete blood count.
"not only in alopecia androgenic females do millions of men and women in this country experience most common causes of hair loss second only to androgenetic alopecia, the hereditary form of balding. Androgenetic alopecia (aga), also known in women as female pattern hair loss, is caused by androgens in genetically susceptible women and men. the thinning begins between ages 12 and 40 years, the inheritance pattern is polygenic, and the incidence is the same as in men.
Komentar
Posting Komentar